Wine and Antioxidants: The Real Story
Wine is an incredibly diverse drink that pairs perfectly with a wide range of meals and occasions. The variety of health benefits in that evening glass of red or white is just a bonus for many consumers.
Discussions about antioxidants in wine are often a part of these conversations about health benefits, but without a clear understanding of wine and its relationship with antioxidants, it can be hard to separate fact from fiction. Here’s what you need to know to make an informed decision when choosing your next bottle.
What Are Antioxidants?
In simple terms, antioxidants are molecules that are produced both within and outside of our bodies. They can be produced naturally during a body’s normal processes but can also be found in certain foods. These molecules can prevent or slow cell damage that causes accelerated aging and disease. The cell damage is caused by a molecular species known as free radicals which are generated as the byproducts of our bodies turning food into energy or by exposure to things like air pollution and sunlight.
At high levels, free radicals can change the instructions coded into our DNA, increase bad cholesterol, and alter the membranes of our cells. This damage is often referred to as oxidative stress and is a possible cause of many serious conditions including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Studies have shown that drinking red wine increases antioxidants and decreases oxidative stress which can, in turn, reduce cell damage. Champagne, which is often referred to as a healthier alternative to wine, also has high amounts of antioxidants, most notably polyphenols.
Antioxidants Found in Red Wines
The discovery of antioxidants happened relatively recently, only beginning to appear in the public eye in the 1990s. Because of this, research is still being done to show how antioxidants work, why they work, and how we can use them to their full potential.
What we do know, however, is that antioxidants come in many different forms that can influence our health in a variety of ways. Similarly, red wines can contain a wide range of different antioxidants at slightly different levels. To fully understand the benefits of the wine you’re drinking, it’s important to learn more about each type of wine through a reputable and knowledgeable source such as a wine club.
Below are some of the main types of antioxidants, their characteristics, and their health benefits that can be found in red wine.
Proanthocyanidins
Proanthocyanidins are chemical compounds that give some fruits and flowers their blue, red, and purple coloring. These compounds have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help prevent cancer. Both red and black grapes contain this compound which is transferred into red wine during the winemaking process.
Research is still being done to quantify the specific health benefits of proanthocyanidins. However, early information points to a connection between diets high in fruit – and thus, high in proanthocyanidins – and a reduced risk of cancer and some age-related conditions. This has led some scientists to believe these chemical compounds can be beneficial for our health.
Further studies are needed to conclusively prove other potential benefits of proanthocyanidins, but theories suggest that they may protect the heart and cardiovascular system as well as block potentially cancer-causing nitrosamines from forming. The compound may also reduce the risk of blood clots, heart attacks, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders.
Quercetin
Quercetin is a naturally occurring component of grape skins and leaves. It’s formed when grapes are exposed to sunlight and protects the fruit from damage caused by ultraviolet rays. Generally speaking, the more sun exposure the plant has, the more quercetin is present. This compound is often responsible for deposits found in aged sangiovese wines, especially when the leaves of the plant are removed to allow for more sun exposure.
In addition to serving as an antioxidant, quercetin is also known to act as an antihistamine, inhibiting allergic and inflammatory reactions. It’s also been shown to slow or prevent the growth of certain cancerous cells, reduce the risk of heart disease, and potentially lower cholesterol levels.
Epicatechin
Epicatechin is a strong antioxidant with a variety of health benefits. Not only does it have similar properties to that of insulin on the cells in our body, but it also has been shown to improve heart health. There’s evidence to suggest that combining epicatechin with other chemicals in mitochondria-targeted therapies has promise in the prevention and treatment of Parkinson’s disease.
Antioxidants Found in White Wines
Red wines are often at the forefront of any conversation about wine and health. However, white wines shouldn’t be left out. White wines have a diverse range of flavors, both bold and subtle, that any wine lover should experience. One way to better understand white wines and appreciate their unique flavors is by hosting or attending a wine dinner where many different wines are paired with a variety of dishes.
Though white wines are made without the skin of the grape which gives red wines their color and many of their health benefits, they still contain a number of antioxidants.
Additionally, because grape skins contain histamine which can cause wine headaches, some individuals find white wine consumption to be more enjoyable. However, some substances are more present in white wine, such as sulfites which can cause allergic reactions in those that are sensitive to sulfur. It’s important to keep these factors in mind when choosing a bottle of wine to purchase.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a compound that is known to have anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and immunomodulatory activities in addition to being a general antioxidant. Wine generally contains large amounts of flavonoids and is believed to be the leading source of flavonoid intake in European countries. This compound is also known to have a direct connection with a 20-30% reduction in mortality, especially when it comes to cardiovascular conditions. Furthermore, studies suggest that flavonoids also have anti-allergic properties.
Research has shown that an appropriate intake of flavonoids may be beneficial when it comes to preventing and possibly even managing allergic conditions. These conditions include things such as atopic dermatitis, asthma, anaphylaxis, and other food allergies. That being said, more studies are needed to confirm these results in humans. Drinks containing alcohol, especially wines, have also been shown to trigger asthma in subjects, leading scientists to caution those with the disease to moderate their consumption.
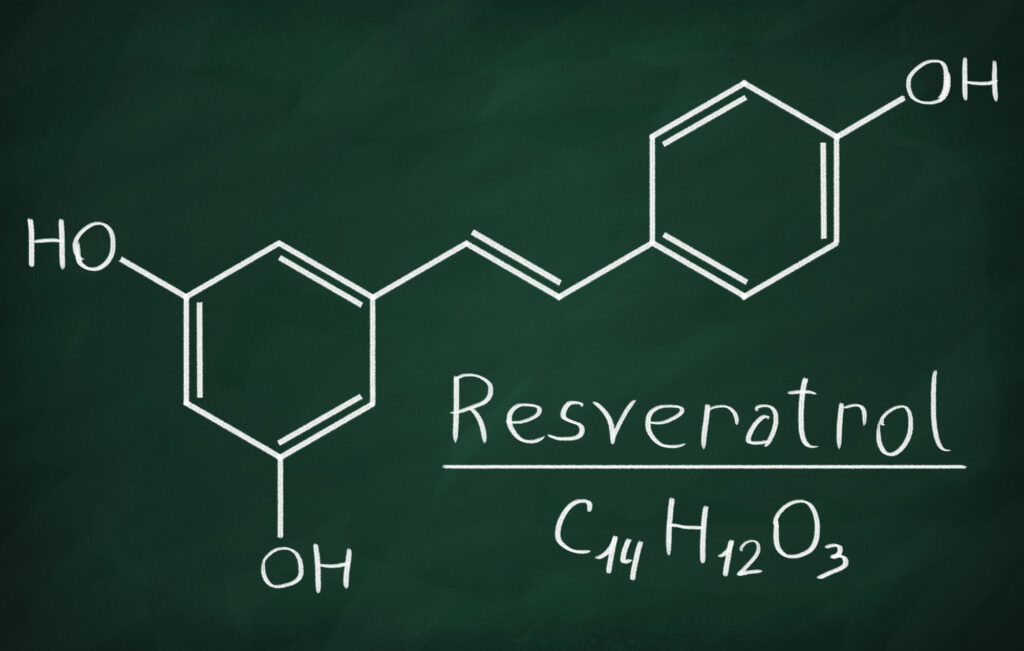
Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a compound found naturally in things like peanuts, grapes, and some berries. Due to the process of making wine and its slight — but significant — variations from winery to winery, white wines contain a variable yet typically low concentration of resveratrol, especially when compared to red wines. That doesn’t mean the levels are completely insignificant, however.
In preclinical studies on resveratrol, this antioxidant has been shown to have certain properties that may help prevent or treat cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases. Though administering resveratrol to living organisms such as fish and mice has increased their lifespans, it’s still unclear how exactly the compound affects humans. To further complicate matters, there have been no clear, consistent test results definitively stating resveratrol’s ability to lower or raise the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Glutathione
Glutathione is a type of tripeptide found in grapes and may be added during the winemaking process, limiting oxidative reactions and preserving the aroma and sensory qualities of the wine. The compound is capable of preventing damage to vital components in our cells caused by several things. Our liver naturally produces certain quantities of glutathione and our bodies use it in everything from building and repairing tissues to immune system function.
It’s not uncommon for people to take glutathione supplements to treat aging, alcohol use disorder, liver disease, heart disease, and many other conditions, though more research is needed to prove its effectiveness. However, it is believed that this compound may help protect against toxic chemicals and prevent cancer.
Caffeic Acid
Caffeic acid is an organic compound found in many plants and foods, most notably apples and coffee. It’s part of a class of micronutrients known for their antioxidant properties. Many believe that this compound has anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and anticancer properties though more research is needed to confirm these hypotheses.
In red wines, caffeic acid is thought to contribute to color stability during the aging process. However, in white wines, the substance is still present and studies have shown that moderate white wine consumption may limit cardiovascular and kidney disease progression because of it.
Though the exact impacts of antioxidants are still being studied alongside their interactions with alcohol found in wines, one thing is certain — drinking wine brings us enjoyment. Many wine lovers will agree that the potential health benefits of wine are just a bonus to the pleasure that can be found in the perfect glass.